The Definitive Guide to What is digital signature and how it works? - Zoho

The Future is Now: Digital Signatures move on to Blockchain Technology
How do I create an electronic signature?
Some Of Electronic signature - Nebraska Legislature
What are digital signatures? Digital signatures resemble electronic "finger prints." In the form of a coded message, the digital signature safely associates a signer with a file in a recorded transaction. Digital signatures utilize a standard, accepted format, called Public Key Facilities (PKI), to offer the greatest levels of security and universal acceptance.
What's the distinction between a digital signature and an electronic signature? The broad classification of electronic signatures (e, Signatures) incorporates many types of electronic signatures. The classification includes digital signatures, which are a specific innovation execution of electronic signatures. Both digital signatures and other e, Signature options enable you to sign documents and verify the signer.

In particular, using digital signature innovation for e, Signatures differs significantly in between nations that follow open, technology-neutral e, Signature laws, consisting of the United States, UK, Canada, and Australia, and those that follow tiered e, Signature designs that prefer in your area specified standards that are based upon digital signature technology, consisting of numerous nations in the European Union, South America, and Asia.
An overview of the concept of Digital Signature Figure 1 describes the - Download Scientific Diagram
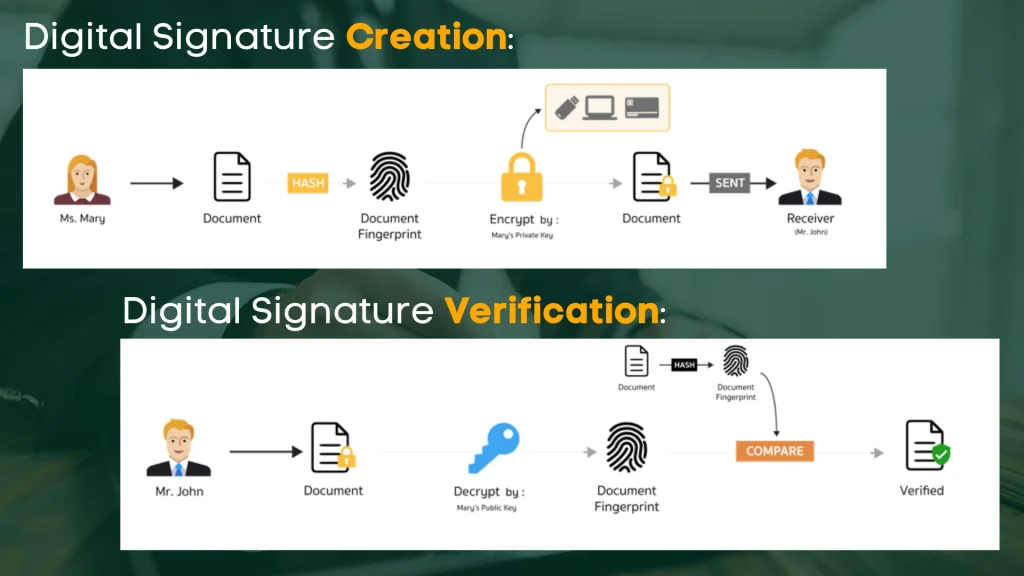
Desire to sign online but do not need a digital signature? How do digital signatures work? Digital signatures, like handwritten signatures, are unique to each signer. Digital signature option companies, such as Docu, Sign, follow a specific procedure, called PKI. apartments requires the company to use a mathematical algorithm to create two long numbers, called keys.
The Greatest Guide To Digital signatures - Cloud KMS Documentation
When a signer electronically signs a document, the signature is produced utilizing the signer's personal key, which is constantly securely kept by the signer. The mathematical algorithm imitates a cipher, producing data matching the signed file, called a hash, and securing that data. The resulting encrypted information is the digital signature.
If the document changes after finalizing, the digital signature is invalidated. As an example, Jane signs an agreement to sell a timeshare using her personal secret. The purchaser receives the document. The buyer who receives the document also receives a copy of Jane's public secret. If the public secret can't decrypt the signature (through the cipher from which the secrets were developed), it implies the signature isn't Jane's, or has actually been altered because it was signed.
